
If you are responsible for corporate information security risk management, we both know your job is tough. Businesses keep generating large volumes of data, IT systems are increasingly complex, and cyber threats continue to evolve. What you have to deal with may sometimes look like an endless number of challenges, and your budget and resources might seem too limited to tackle all of them. Among other things, as an information security leader, you are expected to:
Having a comprehensive information security risk management (ISRM) strategy will help you overcome these challenges. In this post, I will share some tips about how to create an effective ISRM strategy and what a good program looks like. For your convenience, I also provide a FAQ at the end.
Information security risk management is the process of managing the risks associated with the use of information technology. In other words, organizations identify and evaluate risks to the confidentiality, integrity and availability of their information assets. This process can be broadly divided into two components:
Here are three criteria for determining whether your organization’s ISRM strategy is effective at improving your security posture:
What are the steps for creating an effective information security risk management program?
Practice shows that a multi-phased approach to creating an ISRM program is the most effective, as it will result in a more comprehensive program and simplify the entire information security risk management process by breaking it into several stages. It will make the ISRM process more manageable and enable you to fix issues more easily. Here are five steps for building an effective information security risk management program:
First, you need to understand your organization’s business conditions, such as budget considerations, staff and complexity of business processes. I cannot stress the importance of this step enough. Even if you have the best team, tools and controls, you may still fail if you’re not focusing your efforts on what is most important for the business.
During this stage, you have to connect with the organization’s leadership team to understand the business processes and their dependencies on technical assets and data flows. You also need to document the organization’s risk profile, including a detailed description of each risk that it faces as well as its risk appetite — the level of risk it is prepared to accept to achieve its objectives.
This will give you the foundation upon which you can build the ISRM program — and the support of the executives you need to implement it successfully.
Next, your organization needs to define the ISRM program. Be sure to:
In this stage, you need to define the functional capabilities and controls related to IT security and risk management (e.g., vulnerability assessment, incident response, training and communication), along with the governance model that will determine who will be responsible for each area of the ISRM strategy. If you choose to outsource implementation of ISRM capabilities to third parties, be sure consider the risks and ensure appropriate oversight by internal staff.
Next, your organization needs to define the metrics to be used to evaluate the effectiveness of the ISRM strategy. Here are two best practices for this step:
Finally, you should implement your ISRM strategy — and monitor its operation to identify issues or areas for improvement. Define a schedule or conditions for reviewing the program; major changes in your IT environment, data breaches in your industry and new cyberattack techniques are all valid reasons for you to look at your ISRM program with a critical eye and revise it as necessary.
The NIST frameworks are a great resource. Any organization can turn to NIST guidelines to model their own risk management strategy and security baselines. If your organization is looking for a thorough examination of how best practices can be applied through structured regulatory frameworks that also correspond to compliances, you would be well served by studying the NIST Risk Management Framework and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework:
The NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF), as described in NIST Special Publication 800-37 (Revision 2), provides a comprehensive, flexible, repeatable and measurable process for improving how IT systems are designed, secured and monitored. Although the NIST RMF was created by the US Department of Defense (DoD), it serves as a good basis for a data security and privacy plan for any organization.
The NIST RMF involves the following 7 steps (note that last two differ for federal agencies and organizations):

Figure 1. NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF). (from nist.gov/rmf)
Step #1. Prepare
Preparation includes identifying key risk management roles; determining the organization’s risk tolerance; and performing an organization-wide risk assessment of security and privacy risks to the organization from the operation and use of IT systems.
Step #2. Categorize
Next, you need to categorize IT systems by risk level. Estimate the adverse impact of a loss of confidentiality, integrity or availability of systems and the information they process, store or transmit.
Step #3. Select
Based on the results of the previous step, you need to select and implement appropriate controls for each system. During this step, you will make decisions about what baseline security controls you want to implement based on what category the security risks fall into.
Step #4. Implement
The next step is to implement the controls to reduce system security and privacy risks.
Step #5. Assess
Next, it is important that the controls are implemented correctly and operate as expected to protect the systems.
Step #6. Authorize
Step #7. Monitor
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework is another framework that can help companies better manage and mitigate cybersecurity risk. The steps of this framework include the following:
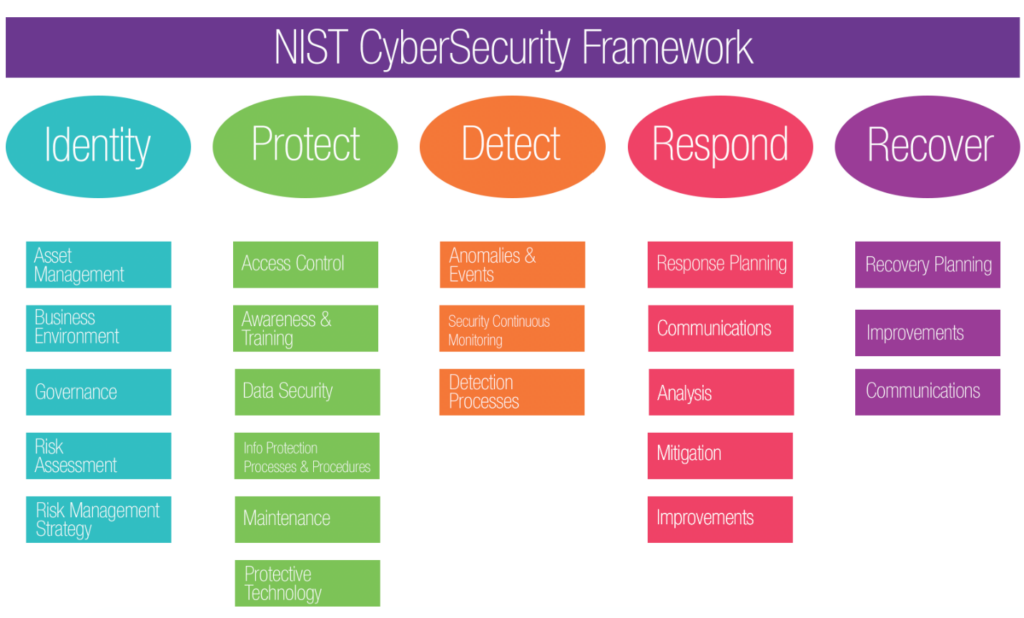
Figure 2. Framework Core Structure image (from the NIST Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity, version 1.1).
Understanding and managing risks to systems and sensitive data is essential for an organization’s success. Developing an ISRM program makes the risk management process more manageable and helps you protect your most critical assets against emerging cyberthreats.
What is risk management in cybersecurity?
Risk management in cybersecurity is managing the security and privacy risks related to information systems. It is a holistic activity that affects every aspect of the organization, including mission planning, enterprise architecture, software development and systems engineering.
What are information security risks?
Information security risks are threats that could can cause damage or disruption to IT systems or data. Common IT security risks are disclosure of passwords, malware and spyware, unauthorized access to the network, and social engineering attacks.
What is the purpose of the NIST Risk Management Framework?
The Risk Management Framework developed by National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) helps organizations build a secure and sustainable ISRM program. It helps them identify and assess the risks to their systems and data, so they can make more informed, risk-based IT security decisions.
Are there any certification programs for the NIST Risk Management Framework?
RMF certification is required only for federal and state agencies, but it can be valuable even if you aren’t employed by the government. Here are a few of the programs can help you learn how to apply the Risk Management Framework in your risk management strategy and get certified if you choose:
How does risk management improve IT security?
A thorough risk management process can strengthen IT security significantly by identifying the risks to an organization’s IT systems and data, and making informed decisions about how to mitigate and eliminate vulnerabilities.
Ilia Sotnikov is Security Strategist & Vice President of User Experience at Netwrix. He has over 20 years of experience in cybersecurity as well as IT management experience during his time at Netwrix, Quest Software, and Dell. In his current role, Ilia is responsible for technical enablement, UX design, and product vision across the entire product portfolio. Ilia’s main areas of expertise are data security and risk management. He works closely with analysts from firms such as Gartner, Forrester, and KuppingerCole to gain a deeper understanding of market trends, technology developments, and changes in the cybersecurity landscape. In addition, Ilia is a regular contributor at Forbes Tech Council where he shares his knowledge and insights regarding cyber threats and security best practices with the broader IT and business community.